Flipkart, the country’s biggest e-commerce company announced the launch of their loyalty program or customer benefits program (as they are calling it) on India’s Independence Day .

Here’s a quick summary of the program
- Opt-in membership with zero fee
- Free Expedited Shipping
- Exclusive access to promotional offers on Flipkart
- Reward points (coins) for purchases on Flipkart, which can be redeemed to buy offers on & off Flipkart (other vendors like Bookmyshow, Cafe Coffee Day)
- Superior & Priority Customer Support


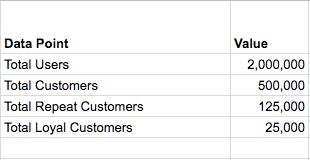
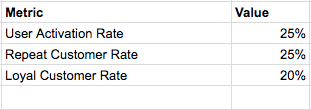
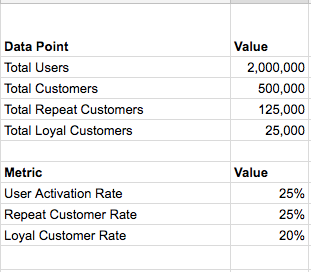
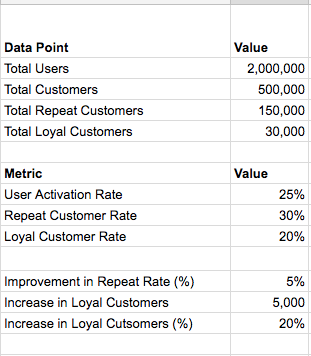
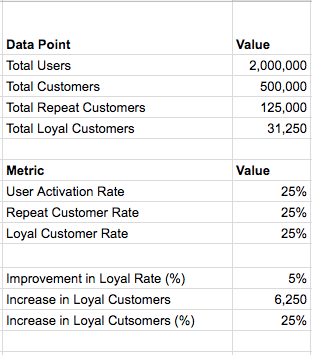
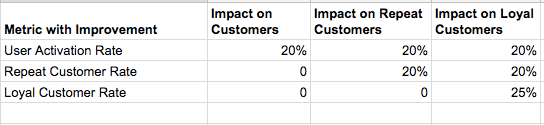
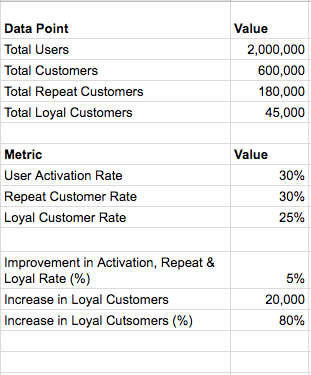
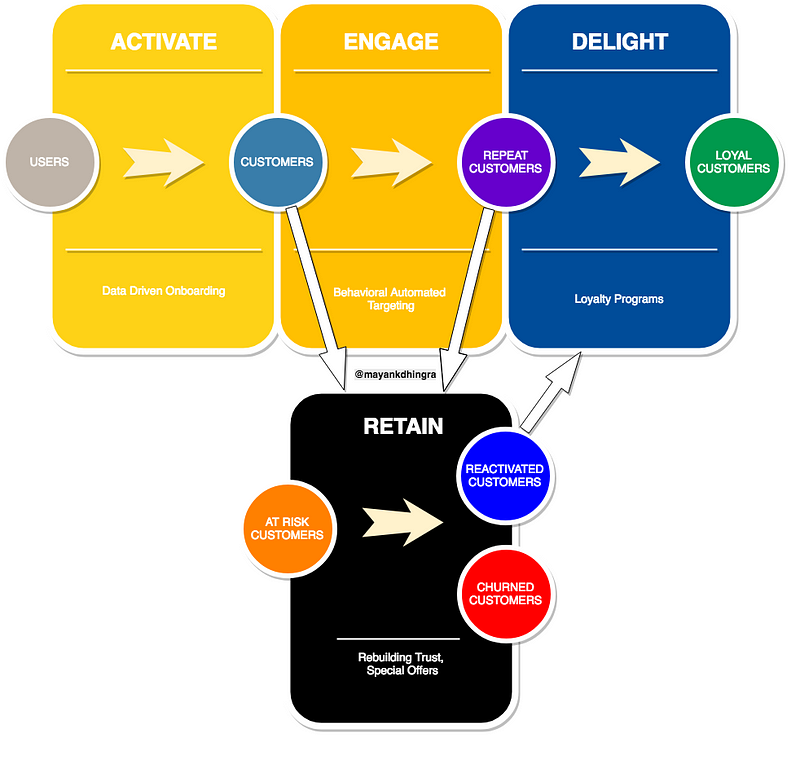
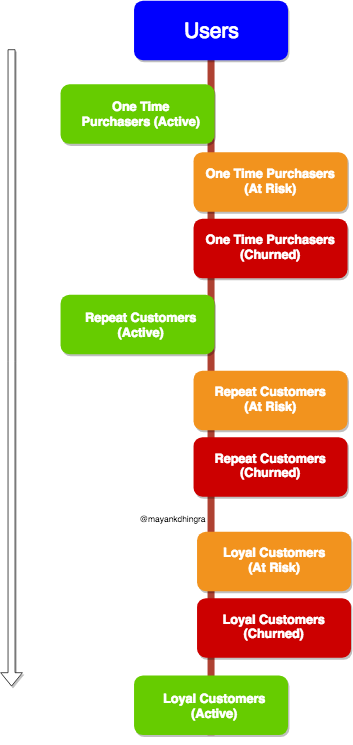
For an e-commerce company to become a sustainable business at scale, customer loyalty (aka retention) is a must. With increased competition and massive customer base, retention is the most obvious and un-avoidable path for all sizeable e-commerce companies, thus the recent public push towards launching loyalty programs.
Coming back to Flipkart, Flipkart Plus is their second attempt to launch a loyalty program. The first attempt was made in 2014.

‘Flipkart First’, ran for 2-3 years before the company quietly setting the sun on it. Since I was an active customer back then, I purchased ‘Flipkart First’ membership twice to avail the benefits.
Here’s a quick overview of how the two programs compare with each other
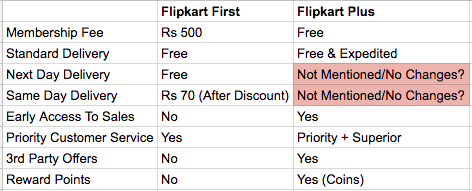
Summarising the key changes:
1. Waving off Membership Fee
2. No commitment over delivery time and charges
3. Adding early access to exclusive deals
4. Superior and Priority customer service
5. Introducing 3rd part offers and reward points
Let’s try to quickly unpack these changes
- Free Memberships:
Positives — Increased Uptake
Negatives — No additional revenue from membership fee
IMO a loyalty program without membership fee is not reflective of brand power and will always restrict goodness you can provide. - Free and Expedited Delivery:
Positives — Increase in both order count (significant) and revenue (insignificant)
Negatives — Extra shippings costs.
Since membership is free and so is shipping, essentially users have no incentive to consolidate their orders and thus they can & will choose to place standalone order for low ticket items but will they spend significantly more because of this, I don’t think so. - Early Access To Exclusive Deals (Actually just Exclusive Deals):
Positives — Depends on quality of deals. Could lead to more orders & revenue
Negatives — The deals on low ticket item products can put further pressure on shipping costs.
The way I see it, I don’t expect great deals for Plus members. Let’s wait and watch on this. - Superior & Priority Customer Service:
Positives — Difficult to measure and communicate value to users. Negatives — If some changes are actually done at CRM, process and team levels. The costs for this could be significant.
Unless a customer buys extremely regularly and interacts with CS often they can’t really see the difference. Even if the experience is better, I’d actually prefer to not having to talk to CS at all.
Also, I’d never want customers to feel they are treated unequally. So generally speaking, I don’t like this feature. - 3rd Party Offers and Reward Points:
Positives — Additional benefit to customers, should bring some additional revenue from 3rd party.
Negatives — The offers currently are unpleasantly few and the usage terms are not friendly (to the point of discouraging impulse use).
Giving formulaic reward points for purchases in form of coins could have been good had they allowed people to redeem them while shopping (think Paytm Cash) but in the current form, users can redeem coins to buy offers on 3rd party or Flipkart. First option currently is un-exciting and second one involves fair amount of friction

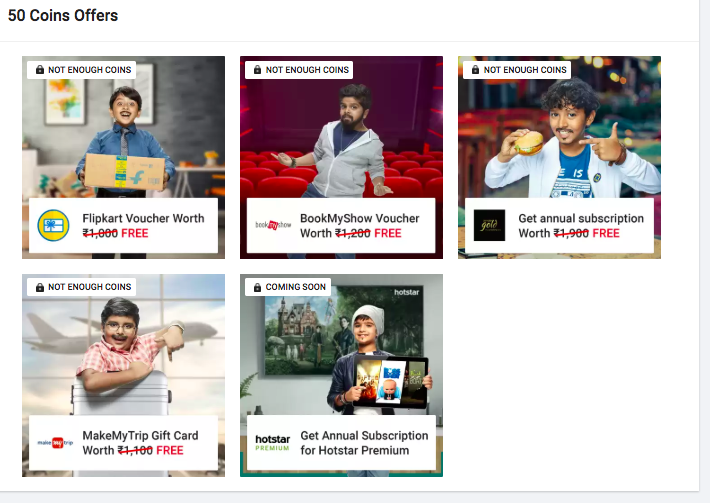
50 Coin Offers
Rs 250 earns you 1 Coin, so you need to spend Rs 12,500 to earn 50 coins.
There’s also a catch, you can’t earn more than 10 coins in an order. So in effect, a user need to place multiple orders (5 big orders or 50 small ones) of Rs 250 or more to accumulate 50 coins.
Once a user has spend Rs 12,500 they are eligible for these offers
– Rs 1000 worth free Flipkart Voucher (8% cashback)
– Rs 1200 worth BMS voucher or Rs 1900 worth Zomato Gold.
These offers are definitely interesting for regular customers as they get all these benefits for free.
Would people spend more often on Flipkart or move to Flipkart because of these benefits (more offers to come) would be interesting to see.